WiseCleaner Think Tank
Encounter difficult computer problems?
All about maintenance and optimization of your Windows System.
Apr 22, 2024
With the information and communication technology development, Wi-Fi has increasingly become a necessity in our daily lives. People who live in mid-size and large homes are searching for a more stable Wi-Fi network that can fully cover all dead zones with the fastest speeds throughout the house, at the same time, relevant manufacturers bring out the mesh technology, a whole home network system, to fill this gap in the market.
Generally speaking, the mesh network is a main route with one or more routes to achieve the effect of expanding the coverage of Wi-Fi. It is built to eliminate dead zones and to provide uninterrupted Wi-Fi throughout your home.

Different from traditional relay or bridge connection transmitting Wi-Fi from a single point, mesh technology has multiple access points within grid-like network nodes, that is when one node fails, it will automatically link to other nodes seamlessly. Thus, mesh routers enable devices in your network to have faster speeds, greater coverage, and a more reliable connection.
Based on different standards of division, mesh Wi-Fi networks can be classified into different types. We will mainly introduce them from the connection method and topology.
A wired mesh network requires cabling to be installed in advance and additional equipment, so the network connection of this networking method will be more stable and faster.
On the contrary, wireless mesh networking is the choice of the vast majority of users, because wireless is more convenient for no need to deploy network cable before the network can work.
A full mesh topology network is one in which each node is directly linked to the other using a purpose-built network topology, meaning all nodes can communicate with each other. It has multiple benefits, including eliminating single points of failure.
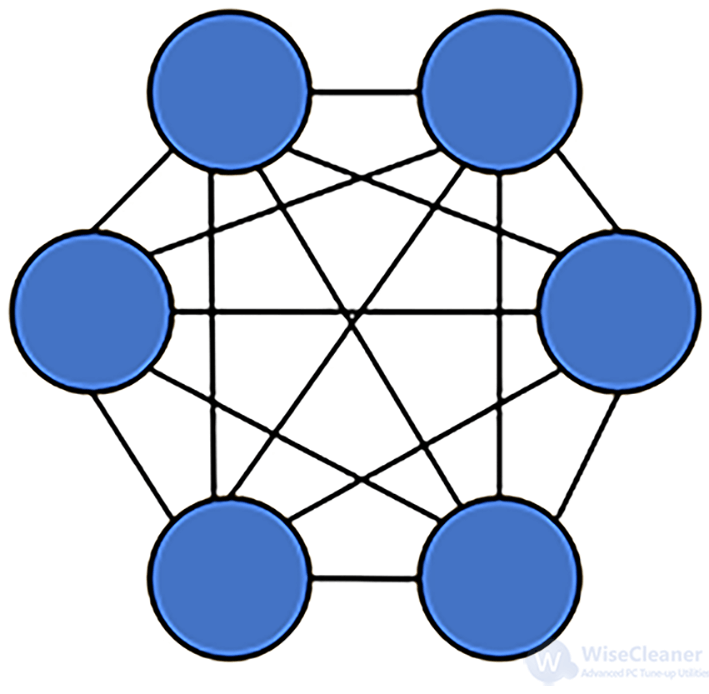
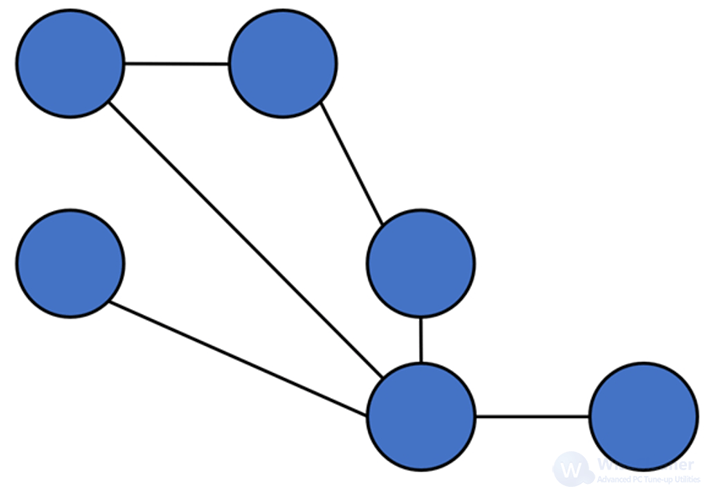
This network allows you to add new devices and scale them up quickly, so it’s functional when you want to extend the range of a network. In addition, partial mesh topology requires less infrastructure and management effort
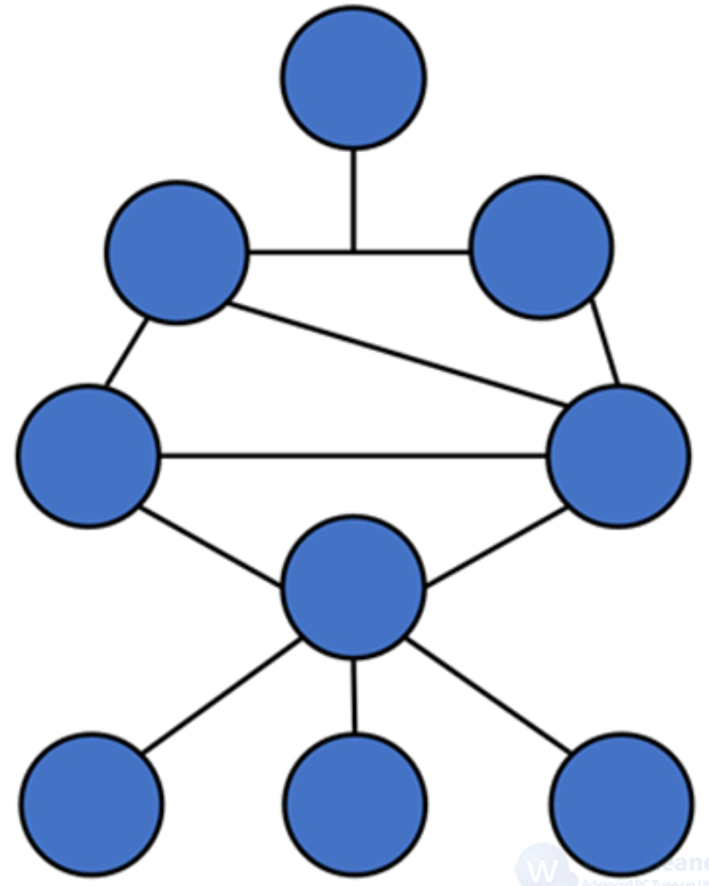
A hybrid topology is always produced when two different basic network topologies are connected. Offering the easiest method for error detecting and troubleshooting, the hydride topology network is scalable for increasing your network size.
Mesh networks can transmit signals over a greater distance. So, they have fewer dead spots where Wi-Fi signals don't reach.
When a node fails, the network structure of mesh Wi-Fi can repair itself and will not affect the normal work of other nodes to ensure the terminal devices connect stably.
With more family members being home, a typical Wi-Fi router will have issues with maintaining a strong internet signal and access to all devices like phones, computers, or TVs. With multiple mesh nodes, everyone can easily connect their devices simultaneously without slowing down the Wi-Fi bandwidth.
Once a mesh network is active, many vendors allow users to control their network system through a mobile app. This could include keeping an eye on network traffic, rebooting, etc.
There are lees to every wine. Mesh Wi-Fi also has weaknesses which are mainly reflected in its price, complex configuration settings, and more.
By contrast, mesh routers are more expensive than traditional Wi-Fi networks for most people.
Mesh networks require strong broadband speeds, making it an unrealistic approach for people living in rural areas and underdeveloped countries. Logically, for these consumers, repeaters and extenders will be the go-to option for Wi-Fi coverage extensions.
Another downside of a mesh Wi-Fi system is that the initial network setup is more demanding. Unlike with a traditional Wi-Fi network, you'll have to position and set up multiple devices, so you need to consider where to put the router and which connection method is better. Therefore, it will take you more time.
Admittedly, mesh network technology brings some surprises for consumers, but it is also not perfect. There are plenty of wireless networking products in the market that can give your home Wi-Fi signal a major boost, so analyze your Wi-Fi needs first to determine which solution is best for your home.
wisecleaner uses cookies to improve content and ensure you get the best experience on our website. Continue to browse our website agreeing to our privacy policy.
I Accept